Latest News
We are devoted to researching and developing the modern signal transmission cable and the joint hardware.
We are devoted to researching and developing the modern signal transmission cable and the joint hardware.
Introducing the HSD144 19-Inch High Density Patch Panel
A next-generation solution engineered for high-efficiency fiber installations.
The HDS144 is designed with a modular architecture and a front/rear push-pull mechanism, enabling fast deployment, easy maintenance, and streamline. Available in 1U, 2U, and 4U configurations, it accommodates up to 576 LC fibers within a standard 19-inch rack.
Independent plug-in cassettes slide smoothly on rails, providing easy front and rear access. The system supports MPO/MTP to LC or MPO/MTP conversion, pigtail splicing, and a variety of connector options — all RoHS compliant.
Ideal for data centers, telecommunications, CATV, and FTTx deployments, the HDS144 offers reliable termination, protection, and management of fiber optic cables while maintaining organized cable routing and optimal airflow.
For inquiries and orders, contact us at: sales@vstech.com.sg
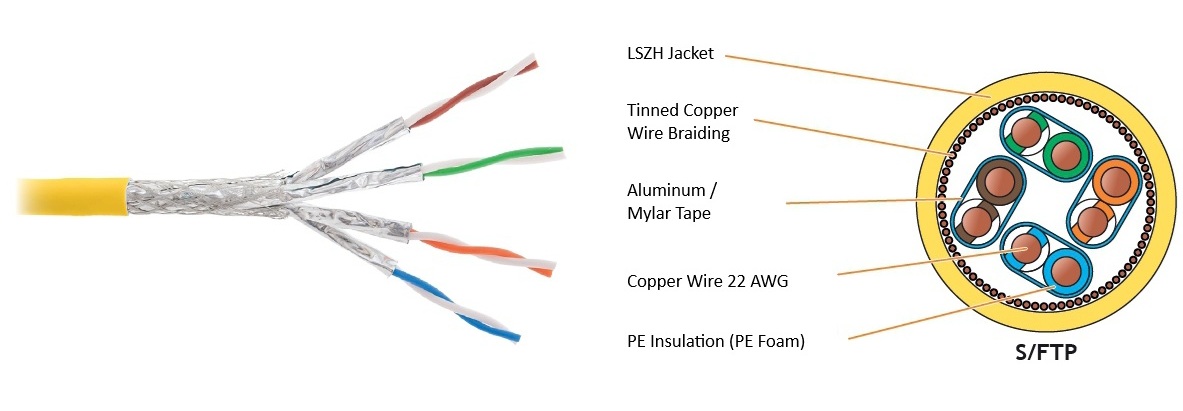
We're excited to introduce the NKL 9385C-YL the newest addition to the NIKOMAX 9th series, now available in ready stock!
This Category 8 S/FTP indoor cable is engineered for ultra-high-speed performance, supporting frequencies up to 2000 MHz — perfect for next-generation Ethernet applications like 25GBASE-T and 40GBASE-T. Each twisted pair is individually shielded to ensure minimal interference and maximum data integrity.
Key Features:
Bandwidth up to 2000 MHz
Individually shielded pairs (S/FTP)
LSZH jacket – flame-retardant, low smoke, and halogen-free
Solid 22 AWG copper conductors
Fully compliant with ISO/IEC, EN, and TIA standards
Supplied on a durable wooden drum for easy installation and safe transport. Available in 500m lengths in high-visibility yellow.
For inquiries and orders, contact us at: sales@vstech.com.sg

Is Your Network Infrastructure Holding You Back?
A fast, secure network is critical to every modern business. But aging cabling systems could be the weak link.
At VS TECH, we offer premium structured cabling using trusted international brands like Premium Line, Nikomax, Netlan, VST —helping you avoid outages, speed up your network and prepare for future growth.
A strong network keeps your business running smoothly. But cables wear out, causing slowdowns and interruptions.
Here are key signs you may need an upgrade:
✔️ Slow or unstable internet
✔️ Frequent network outages
✔️ Old or damaged cables
✔️ Not enough bandwidth for your needs
✔️ Data errors and file transfer issues
✔️ Compatibility problems with new devices
✔️ Network performance issues
✔️ Safety or compliance concerns
✔️ Planning to expand your network
✔️ Security risks
Benefits of Upgrading:
✅ Reliable, high-speed connectivity
✅ Improved security and performance
✅ Ready for future tech demands
✅ Less downtime = more savings
If you recognize any of these signs, don’t wait for a total network failure.
Contact us today for a consultation and customized solution.
Upgrade Today with VS TECH, contact us at sales@vstech.com.sg
Copyright © 2025 VS Tech Pte Ltd. All Rights Reserved.